Miyi County, Sichuan Province has a natural distribution of natural oysters since ancient times. In 1993, the introduction of large-fruit cultivars began to be introduced, and showed four unique advantages of off-season maturation, high soluble solids content, early end-stage high yield, and more resistant storage and transportation. After the county's rapid development in 1998, the industry has now built a total of 1,333 hectares of land. It is planned that by 2010, the expanded planting area of ​​adjacent counties and counties will be increased to 0.67 million hectares, forming a new emerging antimony producing area featuring early season anti-season maturation. Local planting pods, if managed according to the routine, develop from the spring shoots to the resulting mother twigs, flowering from June to December, and fruit ripening from September to April of the following year. The result of flowering is prolonged and the drawbacks are many. Before August, the temperature is higher than the maximum temperature of anther development (20°C). The fruiting rate is very low. Even if it has fruit, the fruit will be too hot and rainy, the fruit will become smaller, the fruit cracking will be more, the soluble solids content will be low, and there will be no commodity value. . The fruit matured after late March will be listed on the same period as Fujian’s early bell No. 6 and lose its anti-season advantage. In order to facilitate the cultivation and management, improve the quality of fruits, and produce batch products at the end of the year, it is necessary to study and popularize the corresponding ripening control technology, so that the pods bloom in September-November and mature from January to March in the following year. The author has been testing for four consecutive years since 1998 and has now initially explored the regulation techniques for the mature period.
Germany imported beads
Imported French lens
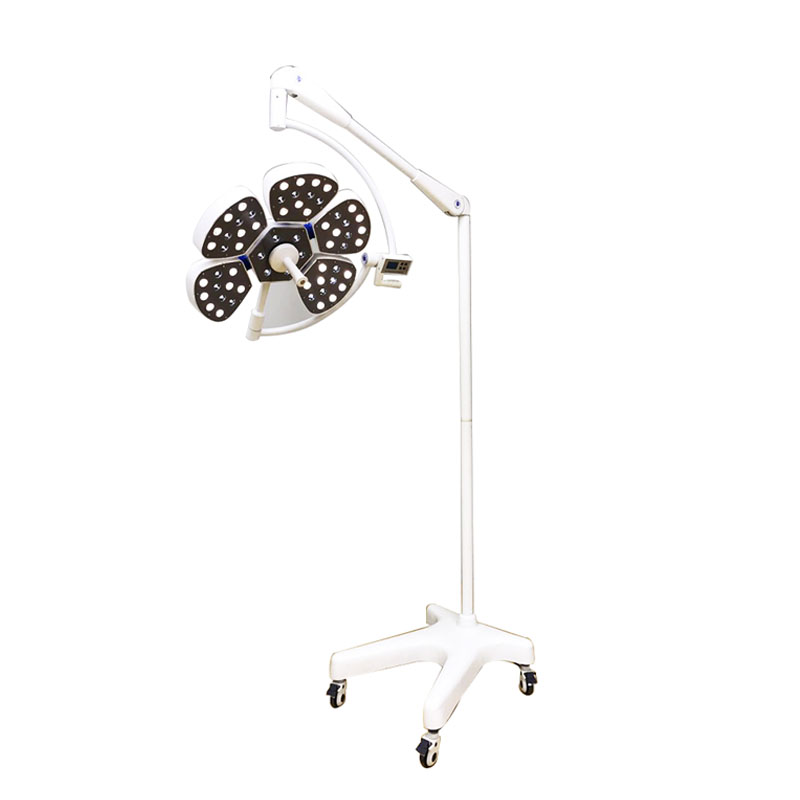
mould Die-casting Eight edge type Revolving arm
Optional emergency power supply≥3 hours
The main features:
1)Ideal cold light effects
Using the new LED cold light source, ensure energy saving and environmental protection and long service life up to 80,000hours and more.
The temperature increase of surgeon`s head below 1℃. LED do not engender infrared ray and ultraviolet radiation, without the temperature
rise and tissue damage caused by halogen shadowless light, also it can accelerate the wound healing after surgery, and without Radiation pollution.
With color temperature constant and soft, LED is very close to the sunshine.
1) Excellent shadowless effect
Lamp with the most scientific radian and Multi point light source design, ensure better uniform illuminance. When the lamps are partially occluded,
also can achieve perfect shadowless effect.Lamp panel radius of gyration ≥182cm, the lamp can be pulled to vertical floor, convenient to any angle illumination.
2) Excellent deep lighting
It is based on modularize method by Computer Aided Design, focused to irradiating with more beams of LED. It produces the deep lighting which beams
more than 1200cm,the illumination of center up to 180,000Lux or more, and offer the color temperature that can be adjusted from 3700K to 5000K which
is close to sunshine. Absolutely, it really reflects the color of human tissue and satisfied by all kinds of operating light needs.
3) Advanced control system
The use of liquid crystal display button control, to meet the needs of the medical staff of different patients with the brightness of the operation.
It offers illuminance memory function.
It does not effect using when a single circuit or one bulb is broken.
4) Universal suspension system
Rotating arm, a new type of alloy material is made of eight edge type.
Balanced system using imported arm module, more than 5 group universal joints, every cantilever must has more than 3 joints which can be rotated in 360°,
The structure is light, easy to manipulate, accurate positioning, can provide the maximum range of regulation.The equipped with fatigue correcting unit and
fix position hand handle device, easy to fix position after long time use.
5) Modern laminar lamp
The thickest part of lamp-chimney is not more than 10cm.
The lamp-chimney is made of ABS, The handle on the central of lamp can be detachable, can take high temperature (≤ 134°C) sterilization treatment,
easily adjust, flexible fixed.
Mobile Type Operating Light,LED Examination Light,Mobile Operation LED Light,Mobile Stand Operating Light Shandong Kang'erjian Medical Technology Ltd. , http://www.operatingtable.nl
1 The main climatic features of the early spring loquat cultivation area are the products of special climate. In the cities of Panzhihua, Liangshan, Lijiang and Chuxiong at the junction of the Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, cultivated alfalfa at an altitude of 1,300-1,700 meters above sea level, the fruits can generally mature in the early spring fruit season by regulating their growth and development. The main climate features of Miyi County, Sichuan Province (East Longitude 10142′~10214′, Northern Latitude 2643′~2716′) and altitudes from 1300 to 1700m are: Annual sunshine hours 2352.5 to 2412.9 hours, and the sunshine percentage is 53% to 55%, of which November The percentage of sunshine in May of the following year was 64.8% to 65.2%, the annual accumulated temperature of ≥10°C was 5555 to 6835°C, the average temperature of the coldest month (January) was 8.7 to 10.8°C, and the temperature in March rose to 15.8 to 18.4°C in November. In March of the following year (fruit development period), the daily temperature difference is 15.6 to 16.3°C; annual rainfall is 1050 to 1353mm, and 6 to 10 months are the rainy season, and rainfall accounts for 80% to 90% of the entire year, from November to May of the following year. For the dry season, the annual average relative humidity is 65% to 70%. Compared with the production areas in Fujian, the cooling in September and the warmth in winter and spring can not only advance the fruit, but also make the fruit grow without stagnation in winter, earlier in the maturation period; the daily temperature is worse, and the soluble solids content is higher; In May, the light is strong and the heat is high (May is the hottest month of the year). With less rainfall and dry atmosphere, it is easy to form early flowers, and corresponding measures must be taken.
2 Test Park Overview and Effects
From 1999 to 2001, the four orchards in the range of 1300 to 1380 m above sea level were tested using the short-stem re-draw parental and the control water and fertilizer supplemented by topping. The results prove that the second scheme is better. In 2002, this program was used to expand the area for testing. The experimental park is 1,320m above sea level with an area of ​​0.4 hectares. The soil is light clay and has a pH of 6.2. Before the park is built, it is a terraced field where the rice is planted. The width of the terrace is 2 to 4m, the slope is 31, and the water source conditions are good. The water can be discharged at any time throughout the year. The tested variety was Big Five Star. In July 1999, the grafted seedlings were planted and the colonization density was 4m3.5m. Mainly layered canopy, leaving a total of 8 main branches in three layers. According to the "3 ~ 3 ~ 2" structure configuration of the main branch, leaving 2 to 3 subsidiary support branches, the spacing from the bottom to the top, respectively, 50,90 and 70cm, tree potential golden mean. Test fruit in 2002, the results of the entire garden in 2003. The branches and branches showed 2 to 3 fruits per ear. The test garden produced 2,102 kg of fruit in 2003, equivalent to 351 kg per 667 square meters. Taking the output per 667 square meters as the statistical unit, the output and quality of different batches are as follows: In 2002, the output of fruit was 2kg, which was 0.57% of the total output. The weight of single fruit was 36g, and the soluble solids content was 12.2%. The fruit production in January 2003 was 83kg, accounting for 23.65% of the total output, 42g of fruit weight, 12.4% of soluble solids; 130kg of fruit produced in February 2003, accounting for 37.04% of the total output, 48g of single fruit weight, 12.8% of soluble solids; March 2003 fruit production 136kg, accounting for 38.74% of the total output, the weight of 52g, soluble solids 11.7%. From March to March, mature fruits accounted for more than 3/4 of the total output and the single fruit weight was the largest.
3 The key to adjusting the maturation period of technical measures is to start from the timing of the results of masterbatch and further adjust the phenology period. To achieve the results from April to May, the mother shoots were withdrawn from May to June. The shoots were planted from July to August. The flowers bloomed from September to November, and the fruits matured from January to March in the following year.
3.1 Control of fertilizers The fertilizer and water must be strictly controlled during the period from late February to early April. This period is the rapid expansion of fruit, the amount of water required for fertilizer, fertilizer and water management to a small amount of ground facilities, to meet the normal growth of fruit. Avoid big fertilizer and partial nitrogen fertilizer. Otherwise, a large number of spring shoots will be promoted in March. These shoots will be stopped in April and flower bud differentiation will be completed in May of high temperature and drought, which will become the mother shoots of spring shoots and will form early flowers from June to July. The practice in Fujian and other producing areas is to promptly promote fertilization after harvesting. Fertilizers can not form fruiting twigs later in the year and affect yield. After harvesting the fruit locally, irrigation and fertilization shall be temporarily suspended. If the water is severely dry and the leaves are drooping until the early morning, the water can still be watered as appropriate.
3.2 Pinching tips On April 15th and 5th days, each strain used 1300g of ammonium bicarbonate, 1000g of superphosphate, 300g of potassium sulfate and 1~5kg of manure. After mixing the superphosphate and the manure, dig five 30cm deep holes along the canopy drip line, apply 5cm deep within the canopy drip line, and pour the bicarbonate ammonia and potassium sulfate to 200kg water. Fertilizer 15 to 20 there will be a lot of new shoots. After picking the fruit and combining pruning and shaping, the top branches with 6 to 8 cm in length and all the leaves have turned green and stopped are subjected to a topping treatment. Two to five axillary buds will germinate after the application of fertilizer, and 1-2 buds will be left after the buds have been cultivated to produce false fruiting branches. 90% of these shoots can form long-term mother trees and bloom in October-November that year. The above-mentioned shoots do not carry out topping treatment and will become the spring shoots resulting in the mother shoots, and flowering is too early to bear fruit.
After the triggering to the onset of the rainy season (early June), it is a severe hot and dry season. Every 10 days, irrigation is conducted once to make the water permeable, and a little water collects in the drainage and irrigation ditch to increase the air humidity. In May, the drought will stop the shoots from reaching their proper length and still form early flowers.
3.3 Stopping and stopping flowering is the premise of flower bud differentiation. June to July coincides with the rainy season. The monthly rainfall is greater than 200mm. Failure to stop the shoot in time will result in leggy leaves, empty nutrient consumption, and reduced yield. At this time, the test garden had no fertilization, no irrigation, and no water in the garden. From the beginning of June, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and water-soluble boric acid 600 times were sprayed on the roots, and sprayed three times. With paclobutrazol 600mg/L root spray once. The garden parked into flowers according to design time.
3.4 After removing the early and late flower buds, there are still some early flowers after adopting the above measures. In the end of June, the entire garden was checked on a plant-by-plant basis. The existing buds should be removed in time and cultivated into vegetative shoots. This period budding to full bloom takes about 60 days, these buds are not removed, will bloom in August, it is difficult to bear fruit. At the same time, the flower buds that appeared after mid-October (which took about 50 days from flower buds to full flowers) were removed to ensure that the flowering period ended in November and the fruit harvesting was completed by the end of March.