The peak of apple flower bud differentiation appeared in the fall. Doing the following four apple tree autumn management measures can lay a solid foundation for the second year's high yield, stable production and high quality. First, fertilizer and water management For unsuccessful trees, 0.15-0.25 kg of diammonium phosphate can be topdressed per plant; as a result, large trees can be produced in accordance with the planned yield for the second year, topdressing 0.7 kg of pure nitrogen and 0.7 kg of available phosphorus per 100 kg of fruit. Sapling dressing can significantly increase the bud rate in the following year. For trees in full fruit period and fertilizing materials in successive autumns, in the case of the same number and type of fertilizers, the yield per tree can be increased by about 50 kilograms compared with that in early summer. In the autumn, combining with the control of apple pests and diseases, 0.3~0.4% urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate can be sprayed twice. In mid-October, 0.3% urea was sprayed on the leaves during the nutrient recirculation period. In September, autumn basal fertilization (late-maturing varieties can be postponed until mid-October), weeds, leaves, diseased fruits, etc., are combined with Shiji fertilizer, and 5% of available N and P fertilizers are applied at the same time. It has a significant effect on improving soil fertility and promoting the growth of apple roots. According to soil moisture, it can be watered in an appropriate amount, and should not be flooded with water so as not to cause long autumn shoots and fruit coloring. In the middle and late November, you can pour a piece of frozen water to help the winter fruit trees. Second, trim Autumn pruning can improve the ventilation and light transmission conditions of trees, increase fruit coloring, improve quality, and have a significant effect on increasing the amount of flower buds in the second year. When the tree canopy is closed, or when there are too many outer upper shoots affecting the light, thinning, shrinking part of the young shoots, long branches and long branches. The long shoots left after thinning can be softened in late August to change its growth polarity. If the tree body is too tall and there are too many supplementary branches and branches, the heads can be properly dropped and cleaned after the fruit is picked, but the quantity should not be too much. Autumnal branches are more likely to form flower buds than spring pull branches, and at the same time can avoid producing a large number of backside branches. Pull branches on lateral branches of unsuccessful trees, generally 70 to 80 degrees. The pull-branch has the effect of improving lighting, stopping the growth of long shoots, enriching new shoots, and reducing winter shear workload. Third, pest control The main pests of apple trees in autumn include peach borer, boat-shaped caterpillar, gold-lined moth, and big leafhopper, etc. Diseases include ringworm disease, anthrax, and rot disease. The rot disease is now at the peak of the second (autumn) incidence in the whole year, and must be promptly scraped off and coated with drugs for prevention and treatment. For other pests and diseases, we must combine the local pest situation and disease conditions, do a good job of comprehensive prevention and control, and increase the rate of good fruit. This will also have a significant effect on preventing the saplings of young trees and improving the winter cold resistance of the trees. It should be pointed out that after entering 8 to 9 months, it is best not to spray Bordeaux mixture, so as not to affect the coloration of red varieties. Fourth, improve fruit quality For red cultivars, such as Marshal and Fuji, in the late growth stage, a silver-grey reflective film is applied to the canopy to enhance the reflected light; the shaded leaves near the fruit are removed twice and 20 to 30 days before fruit harvest. Careful fruit transfer will help increase the coloration of red varieties and improve fruit quality. In addition, post-growth fertilizers such as potassium dihydrogen phosphate, Gaomeishi and Yemianbao can also increase fruit coloring. Why choose the sapphire?
Sapphire Customized,Optical Sapphire Customized,Customized Optical Sapphire,Customized Optical Sapphire Lens ChangChun Worldhawk Optics Co.,Ltd , https://www.worldhawk-optics.com
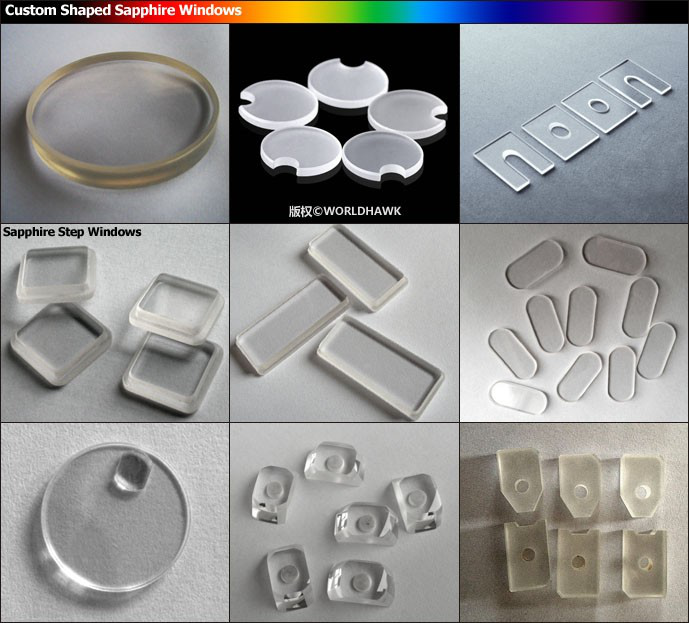
1-Thinner and Stronger than Standard Glass Windows
2-Transmits Wavelengths Ranging From UV to Mid-Infrared
3-Features Extreme Surface Hardness and Chemical Resistance
Sapphire Windows are manufactured from single crystal sapphire, making them ideal for demanding applications (such as laser systems) because of their extreme surface hardness, high thermal conductivity, high dielectric constant and resistance to common chemical acids and alkalis. Sapphire is the second hardest crystal next to diamonds and, because of their structural strength, sapphire windows can be made much thinner than other common dielectric windows with improved transmittance. Chemically, sapphire is single crystal aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and is useful in a transmission range from 0.2 - 5.5µm.
Applications:
Sapphire Washers
Sapphire Windows
Sapphire Bearings
Sapphire Rods
Sapphire Tubes
Sapphire Wafer
Dome sapphire
Sapphire insulation Film