An anesthetic (or anaesthetic) is a drug to prevent pain during surgery, completely blocking any feeling as opposed to an analgesic. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesia, although others are used commonly by all disciplines. Anesthetics are categorized into two classes: general anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body while maintaining consciousness. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. We produce anesthetic raw materials like tetrcacain, lidocaine prilocaine. These three anesthesia products are in commercial quantity.
Prilocaine structure:
Tetracaine Anesthetic Drug,Anesthetic Powder,Anesthetic Cream Pharmaceuticals,Bupivacaine Base Anesthetic Pharmaceuticals Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd. , http://www.pharmachemm.com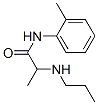
Precautionary measures for wheat lodging
There are two types of wheat lodging, root lodging and stem lodging. The stem lodging was caused by excessive seeding, high population density, crowded wheat and tillers, poor light transmission, improper fertilization, excessive nitrogen fertilizer, etc., which caused the stem base of wheat to be bent and tilted to lodging. This kind of lodging is more common in production. The prevention method is as follows: Early prediction of wheat lodging The seeding rate is too large. The seedlings per 667 m M2 (1 mu) basic seedlings exceed 400,000, and the wheat fields over the wintering period over 800,000 have the possibility of lodging; from the wheat seedling growth From the above point of view, when the sagging length of the first and second leaves of the base reaches more than one-third of the total leaves, wheat is in danger of lodging. In addition to the selection of lodging-resistant varieties and proper close planting, preventive measures for wheat lodging should also include the following measures: Control of fertilizer and water. For young and large-scale wheat seedlings, strict control of nitrogen fertilizer after returning green, appropriate application of some phosphorus and potassium to promote root development; for the lack of base fertilizer, barren land, and relatively weak wheat fields, it is necessary to take measures to promote control and integration. Controlling the return of green manure to see if the seedlings supplemented the drawing joints, the booting of the panicles, and the promotion of robust growth of the plants; for the excessive use of nitrogen fertilizer in wheat fields, it is necessary to control the irrigation to prevent the greed green from ripening and lodging. Sparse seedlings cut off the roots. For wheat fields with overgrowth or large groups, the seedlings must be sparsely planted in advance before winter to strengthen their control; after cultivating, further deep cultivating, cutting off part of the old roots, promoting new root growth and development, and enhancing the lodging resistance of wheat. Timely suppression. For young seedlings with overgrowth and seedless tendencies during seedling stage, they may be appropriately repressed before wintering to jointing to shorten the length of the first internodes of the stem base, reduce the plant height, thicken the stem wall, and enhance mechanical toughness; Too large to prevent lodging due to prosperous growth. Rational control. Paclobutrazol can not only control the length of wheat, dwarf the plant type, prevent lodging, increase the yield, and can also treat wheat powdery mildew. During the effective period, the sooner the application is, the better the effect will be. The use of a concentration of: strong growing wheat fields with 667 meters M2 with 40-50 grams, less prosperous every 667 meters M2 with 30-40 grams, are 30-40 kg of water spray, less than 20 grams of poor results, greater than 60 grams are prone to excessive suppression.