Digital Operation Room use advanced technology, doctor can get patient`s related import information real-time, no matter examining PACS imaging, getting hemodynamic test data from sterile area, or remote assist surgeon on other place, real-time consulting with pathology or ICU
Operation room is designed for surgeon, nurse, especially for patient making best operation environment. Integrated operation room can improve working efficiency and ergonomic conditions. Different operations special equipments requirement and information center requirement promote digital operation room rapidly development
Every operation room can be designed according requirement, suitable for multiple professions or single profession, such as neurosurgery, cardiac surgery, orthopedics, pediatrics, general surgery and gynecology
For more information about Operating Light, Operating Table, Hospital Bed and Medical Pendant please visit website.
Digital Operation Room Digital Operation Room,Dialysis Bed,Operating Room Equipment,Led Operating Room Shandong Mingtai Medical Equipment Group Co., Ltd , http://www.mingtaic.com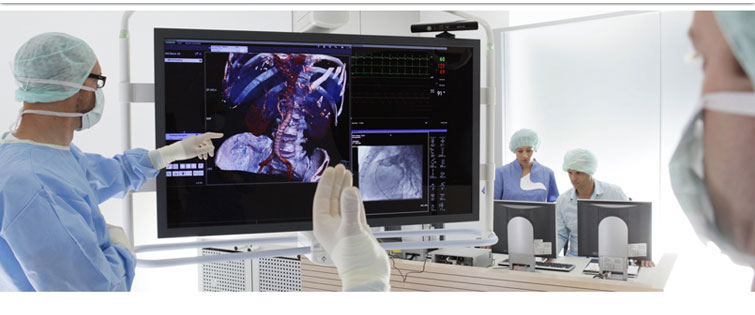
Parsley cultivation technology
Parsley is an aphrodisiac herbaceous plant of the genus Ovrycum, which is also known as artichoke, parsley, dry celery, and citron. The color of parsley is green and has a clear fragrance. Its edible parts are young leaves and tender stems, which can be eaten raw or cooked with meat. It can also be used as a dry and fragrant seasoning for dishes or as a seasoning for soups and other vegetable foods, and has been welcomed by people. I. Biological characteristics (1) Botanical characteristics The height of the parsley plants is 50-60 cm. The roots are straight, and the main roots are buried in 45 cm. The leaves are rooted out of three feather-like compound leaves. The leaflets are deeply nicked and the leaf edges are serrated. Shrink, petiole 10 cm long, 0.5 cm thick, inflorescences umbrella-shaped, flowers small white, bisexual flowers, seeds small, dark brown. (b) Requirements for environmental conditions Parsley prefers a warm and cool environment. The growth and development temperature is 5 to 35°C, the optimum temperature is 15 to 20°C, and the growth is slower than 28°C. Freezing in the long term is less than -2°C. . The growth stage is hi moist but not stain resistant. More shade-tolerant, but sufficient light, strong growth. Wide adaptability to soil, good growth in the range of pH 6-8, more demand for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, more sensitive to boron, boron deficiency can cause cracking of petiole base. (III) Growth and development cycle The vegetative growth period of parsley is roughly divided into two phases. 1. Seedling seed sowing after sowing enough water, at a temperature of about 25 °C 7 days can emerge, grow to 5 ~ 7 leaves become seedlings. 2. When the parsley has a certain area during the growth period, the heart leaves continue to grow, forming a peak, the vegetative body increases rapidly, and the leaf buds on the short-thinning stems of the base gradually differentiate and draw out the leaves, the plants show a plexiform shape, and the absorption force is enhanced. It can grow more than 50 leaves. Second, the selection of varieties of parsley leaves wrinkled leaves and leaves of the points, the species can also be divided, the common varieties are as follows. 1. No.1 celery was introduced from Japan. Strong growth, tall plants, high yield, wide petiole, thick leaves, not easy to aging, bright green, good appearance, late bolting, strong disease resistance, easy to cultivate. Pay attention to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. 2. Bryan Oh introduced from Denmark. The leaves are curly black-green, good quality, and strong cold resistance. They can be harvested after sowing for about 90 days and can be harvested gradually. 3. Karelin was introduced from Denmark. Short stems, curly leaves, long green color after ripening, high content of essential oils and dry matter, suitable for fresh-selling and quick-freezing. Easy to cultivate. 4. Afraid of Wu Si from Denmark. The leaves are dark green, densely coiled, with solid stems and high yields, suitable for cultivation in hot and humid climates. Third, cultivation techniques (a) cultivation season parsley can be cultivated in open spring and autumn. The use of protective facilities; can be cultivated throughout the year. (2) Seedlings firstly prepare seedbeds to keep bed soil loose, then use 1000kg of manure and ash in Mushi, turn over evenly, the seeding rate per square meter of seedbed is 2~2.5g, and the planting field per acre needs 13~15. G, covered with thin soil after sowing. The spring sowing can be covered with a plastic film and a small shed. After the seedlings are lifted, the plastic film is peeled off. In the summer and autumn, the seedlings are shaded or shaded and used to cool and moisturize. In 5-6 leaves, it can be planted in the field. If live cultivation is used, seedlings should be seedlings. (c) Planting and Management Planting method of planting the field, to ensure that the soil is loose and avoid heavy weight. Before planting, 2000 kg of pig manure was applied, 1000 kg of human and animal manure, 25 kg of superphosphate, 5 kg of potassium sulfate, ridges after turning and hoeing, 1.2 m wide, 15 cm spacing and 20 cm spacing, and 1 mu planting density. 80000 strains. 2. After the planting of fertilizers and waters, planting water shall be planted after planting for about 3 days. After 7 days, new leaves will be sprouted to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. In the period of vigorous growth, in addition to watering, we must apply appropriate amount of fertilizer, applying 3 kg of urea per acre, and spray 0.3% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate on the leaves at the same time. After harvest, we still have to top-dress and promote growth. . 3. When cultivating and weeding soil compaction, early cultivating and weeding should be done, so it should not be too deep so as not to damage the roots. Generally, it is carried out after harvesting. 4. Diseases and insect pests control disease spots disease, can be used 400 times liquid control Sen Zinc. In the case of high temperatures and nutrient susceptibility, they are prone to physical diseases. If potassium deficiency, boron deficiency, etc., spraying 0.2% phosphoric acid: potassium dihydrogen and 0.1% borax can relieve the development of symptoms. Insect pests are maggots and carrot flies. Aphids can be used to kill and kill fleas 6000 times or 2.5% Kung Fu EC 4000 times; carrot flies can be used 20% Juma EC 3000 times, 90% trichlorfon crystals or 80% enemy 100 Insect soluble powder 1000 times, 50% Dimethoate 1000 times, 25% synergist quinolone emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times Irrigation control. (4) Harvesting and harvesting are generally carried out during the vigorous growth period. The method is to cut out the external growth leaves, the base leaves a petiole about 1 cm long. The harvesting standard is that when the plant has 14 green leaves or more, it can pick the middle leaf with moderate growth and good commercial character, generally 3 to 4 leaves in the middle is appropriate. Most of the base leaves are not suitable for harvesting the old leaves. The upper leaves are young, not fully stretched, and the single leaf is relatively light and the efficiency is poor. When the lower leaves are yellow and the number of green leaves is reduced, they should be collected as little as possible to increase the photosynthesis needs. The leaf area. Is a biennial herb of the genus Ovulaceae from the Umbelliferae family. The color of parsley is green and has a clear fragrance. Its edible parts are young leaves and tender stems, which can be eaten raw or cooked with meat. It can also be used as a dry and fragrant seasoning for dishes or as a seasoning for soups and other vegetable foods, and has been welcomed by people. I. Biological characteristics (1) Botanical characteristics The height of the parsley plants is 50-60 cm. The roots are straight, and the main roots are buried in 45 cm. The leaves are rooted out of three feather-like compound leaves. The leaflets are deeply nicked and the leaf edges are serrated. Shrink, petiole 10 cm long, 0.5 cm thick, inflorescences umbrella-shaped, flowers small white, bisexual flowers, seeds small, dark brown. (b) Requirements for environmental conditions Parsley prefers a warm and cool environment. The growth and development temperature is 5 to 35°C, the optimum temperature is 15 to 20°C, and the growth is slower than 28°C. Freezing in the long term is less than -2°C. . The growth stage is hi moist but not stain resistant. More shade-tolerant, but sufficient light, strong growth. Wide adaptability to soil, good growth in the range of pH 6-8, more demand for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, more sensitive to boron, boron deficiency can cause cracking of petiole base. (III) Growth and development cycle The vegetative growth period of parsley is roughly divided into two phases. 1. Seedling seed sowing after sowing enough water, at a temperature of about 25 °C 7 days can emerge, grow to 5 ~ 7 leaves become seedlings. 2. When the parsley has a certain area during the growth period, the heart leaves continue to grow, forming a peak, the vegetative body increases rapidly, and the leaf buds on the short-thinning stems of the base gradually differentiate and draw out the leaves, the plants show a plexiform shape, and the absorption force is enhanced. It can grow more than 50 leaves. Second, the selection of varieties of parsley leaves wrinkled leaves and leaves of the points, the species can also be divided, the common varieties are as follows. 1. No.1 celery was introduced from Japan. Strong growth, tall plants, high yield, wide petiole, thick leaves, not easy to aging, bright green, good appearance, late bolting, strong disease resistance, easy to cultivate. Pay attention to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. 2. Bryan Oh introduced from Denmark. The leaves are curly black-green, good quality, and strong cold resistance. They can be harvested after sowing for about 90 days and can be harvested gradually. 3. Karelin was introduced from Denmark. Short stems, curly leaves, long green color after ripening, high content of essential oils and dry matter, suitable for fresh-selling and quick-freezing. Easy to cultivate. 4. Afraid of Wu Si from Denmark. The leaves are dark green, densely coiled, with solid stems and high yields, suitable for cultivation in hot and humid climates. Third, cultivation techniques (a) cultivation season parsley can be cultivated in open spring and autumn. The use of protective facilities; can be cultivated throughout the year. (2) Seedlings firstly prepare seedbeds to keep bed soil loose, then use 1000kg of manure and ash in Mushi, turn over evenly, the seeding rate per square meter of seedbed is 2~2.5g, and the planting field per acre needs 13~15. G, covered with thin soil after sowing. The spring sowing can be covered with a plastic film and a small shed. After the seedlings are lifted, the plastic film is peeled off. In the summer and autumn, the seedlings are shaded or shaded and used to cool and moisturize. In 5-6 leaves, it can be planted in the field. If live cultivation is used, seedlings should be seedlings. (c) Planting and Management Planting method of planting the field, to ensure that the soil is loose and avoid heavy weight. Before planting, 2000 kg of pig manure was applied, 1000 kg of human and animal manure, 25 kg of superphosphate, 5 kg of potassium sulfate, ridges after turning and hoeing, 1.2 m wide, 15 cm spacing and 20 cm spacing, and 1 mu planting density. 80000 strains. 2. After the planting of fertilizers and waters, planting water shall be planted after planting for about 3 days. After 7 days, new leaves will be sprouted to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. In the period of vigorous growth, in addition to watering, we must apply appropriate amount of fertilizer, applying 3 kg of urea per acre, and spray 0.3% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate on the leaves at the same time. After harvest, we still have to top-dress and promote growth. . 3. When cultivating and weeding soil compaction, early cultivating and weeding should be done, so it should not be too deep so as not to damage the roots. Generally, it is carried out after harvesting. 4. Diseases and insect pests control disease spots disease, can be used 400 times liquid control Sen Zinc. In the case of high temperatures and nutrient susceptibility, they are prone to physical diseases. If potassium deficiency, boron deficiency, etc., spraying 0.2% phosphoric acid: potassium dihydrogen and 0.1% borax can relieve the development of symptoms. Insect pests are maggots and carrot flies. Aphids can be used to kill and kill fleas 6000 times or 2.5% Kung Fu EC 4000 times; carrot flies can be used 20% Juma EC 3000 times, 90% trichlorfon crystals or 80% enemy 100 Insect soluble powder 1000 times, 50% Dimethoate 1000 times, 25% synergist quinolone emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times Irrigation control. (4) Harvesting and harvesting are generally carried out during the vigorous growth period. The method is to cut out the external growth leaves, the base leaves a petiole about 1 cm long. The harvesting standard is that when the plant has 14 green leaves or more, it can pick the middle leaf with moderate growth and good commercial character, generally 3 to 4 leaves in the middle is appropriate. Most of the base leaves are not suitable for harvesting the old leaves. The upper leaves are young, not fully stretched, and the single leaf is relatively light and the efficiency is poor. When the lower leaves are yellow and the number of green leaves is reduced, they should be collected as little as possible to increase the photosynthesis needs. The leaf area. Is a biennial herb of the genus Ovulaceae from the Umbelliferae family. The color of parsley is green and has a clear fragrance. Its edible parts are young leaves and tender stems, which can be eaten raw or cooked with meat. It can also be used as a dry and fragrant seasoning for dishes or as a seasoning for soups and other vegetable foods, and has been welcomed by people. I. Biological characteristics (1) Botanical characteristics The height of the parsley plants is 50-60 cm. The roots are straight, and the main roots are buried in 45 cm. The leaves are rooted out of three feather-like compound leaves. The leaflets are deeply nicked and the leaf edges are serrated. Shrink, petiole 10 cm long, 0.5 cm thick, inflorescences umbrella-shaped, flowers small white, bisexual flowers, seeds small, dark brown. (b) Requirements for environmental conditions Parsley prefers a warm and cool environment. The growth and development temperature is 5 to 35°C, the optimum temperature is 15 to 20°C, and the growth is slower than 28°C. Freezing in the long term is less than -2°C. . The growth stage is hi moist but not stain resistant. More shade-tolerant, but sufficient light, strong growth. Wide adaptability to soil, good growth in the range of pH 6-8, more demand for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, more sensitive to boron, boron deficiency can cause cracking of petiole base. (III) Growth and development cycle The vegetative growth period of parsley is roughly divided into two phases. 1. Seedling seed sowing after sowing enough water, at a temperature of about 25 °C 7 days can emerge, grow to 5 ~ 7 leaves become seedlings. 2. When the parsley has a certain area during the growth period, the heart leaves continue to grow, forming a peak, the vegetative body increases rapidly, and the leaf buds on the short-thinning stems of the base gradually differentiate and draw out the leaves, the plants show a plexiform shape, and the absorption force is enhanced. It can grow more than 50 leaves. Second, the selection of varieties of parsley leaves wrinkled leaves and leaves of the points, the species can also be divided, the common varieties are as follows. 1. No.1 celery was introduced from Japan. Strong growth, tall plants, high yield, wide petiole, thick leaves, not easy to aging, bright green, good appearance, late bolting, strong disease resistance, easy to cultivate. Pay attention to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. 2. Bryan Oh introduced from Denmark. The leaves are curly black-green, good quality, and strong cold resistance. They can be harvested after sowing for about 90 days and can be harvested gradually. 3. Karelin was introduced from Denmark. Short stems, curly leaves, long green color after ripening, high content of essential oils and dry matter, suitable for fresh-selling and quick-freezing. Easy to cultivate. 4. Afraid of Wu Si from Denmark. The leaves are dark green, densely coiled, with solid stems and high yields, suitable for cultivation in hot and humid climates. Third, cultivation techniques (a) cultivation season parsley can be cultivated in open spring and autumn. The use of protective facilities; can be cultivated throughout the year. (2) Seedlings firstly prepare seedbeds to keep bed soil loose, then use 1000kg of manure and ash in Mushi, turn over evenly, the seeding rate per square meter of seedbed is 2~2.5g, and the planting field per acre needs 13~15. G, covered with thin soil after sowing. The spring sowing can be covered with a plastic film and a small shed. After the seedlings are lifted, the plastic film is peeled off. In the summer and autumn, the seedlings are shaded or shaded and used to cool and moisturize. In 5-6 leaves, it can be planted in the field. If live cultivation is used, seedlings should be seedlings. (c) Planting and Management Planting method of planting the field, to ensure that the soil is loose and avoid heavy weight. Before planting, 2000 kg of pig manure was applied, 1000 kg of human and animal manure, 25 kg of superphosphate, 5 kg of potassium sulfate, ridges after turning and hoeing, 1.2 m wide, 15 cm spacing and 20 cm spacing, and 1 mu planting density. 80000 strains. 2. After the planting of fertilizers and waters, planting water shall be planted after planting for about 3 days. After 7 days, new leaves will be sprouted to keep the soil moist and avoid drought. In the period of vigorous growth, in addition to watering, we must apply appropriate amount of fertilizer, applying 3 kg of urea per acre, and spray 0.3% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate on the leaves at the same time. After harvest, we still have to top-dress and promote growth. . 3. When cultivating and weeding soil compaction, early cultivating and weeding should be done, so it should not be too deep so as not to damage the roots. Generally, it is carried out after harvesting. 4. Diseases and insect pests control disease spots disease, can be used 400 times liquid control Sen Zinc. In the case of high temperatures and nutrient susceptibility, they are prone to physical diseases. If potassium deficiency, boron deficiency, etc., spraying 0.2% phosphoric acid: potassium dihydrogen and 0.1% borax can relieve the development of symptoms. Insect pests are maggots and carrot flies. Aphids can be used to kill and kill fleas 6000 times or 2.5% Kung Fu EC 4000 times; carrot flies can be used 20% Juma EC 3000 times, 90% trichlorfon crystals or 80% enemy 100 Insect soluble powder 1000 times, 50% Dimethoate 1000 times, 25% synergist quinolone emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times Irrigation control. (4) Harvesting and harvesting are generally carried out during the vigorous growth period. The method is to cut out the external growth leaves, the base leaves a petiole about 1 cm long. The harvesting standard is that when the plant has 14 green leaves or more, it can pick the middle leaf with moderate growth and good commercial character, generally 3 to 4 leaves in the middle is appropriate. Most of the base leaves are not suitable for harvesting the old leaves. The upper leaves are young, not fully stretched, and the single leaf is relatively light and the efficiency is poor. When the lower leaves are yellow and the number of green leaves is reduced, they should be collected as little as possible to increase the photosynthesis needs. The leaf area.